DNA synthesis bind to specific regions of the chromosomes which is the replication origin.In prokaryotes there is only one origin for replication. The small chromosomes can replicate rapidly. Eukaryote although contain several chromosomes. Once the DNA double helix is at the origin and separates, an enzyme starts for preparation of each of the individual strands of DNA for synthesis. When the replisome moves away from the replication origin it starts to unwind the double helix. The replisomes move away from the replication origin along the DNA in both directions. The results of the process replaces the old DNA double helix with 2 identical ones. After adding a new nucleotide to the chain it goes through a check point to see if everything is correct. And if there is an error in the enzyme, the enzyme will put everything in a stand still and it'll remove the nucleotide and replace it with a correct one. If there is a mutation the enzyme would bind it to DNA and it'll break the sugar phosphates bonds of the mutation and fix it correctly.
Transcription:
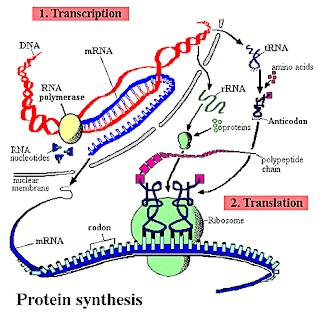
(is the process of the making of a mRNA molecule) Happens in three stages the Initiation is the 1st stage. Its occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerse attaches to a specific region of the DNA. This are is known as the promteter region. But in the eukaryote cells the proteins need to present for the RNA polymerse to join itself with the prometer region. The 2nd stage is known as the Elongation. The Elongation is when the RNA polymerse begins to break the DNA. The enzyme travels with the DNA away from the prometer. A strand of RNA is created known as the primary transcript. The 3rd stage is known as Termination. Its when the RNA polymerse reaches at the end of the DNA to be transcribed. The primary transcript and the enzyme id then released.
Translation: When the protein synthesis moves the codon sequence of the mRNA to the amino acid sequence of a protein. One end of the RNA molecule carries a specific amino acid and the other side is the anti codon. The anti codon pairs with the mRNA . When the correct amino acid conbines with tRNA is called tRNA charging. Each enzyme bonds a different amino acid to its match tRNA by the energy from ATP. The tRNA and mRNA and the polypeptide chain come together at a specific region on the ribosomes. The tRNA leaves the E site after its amino acid is added to the polypeptide chain. The ribosomes move along the mRNA strand at a time.
Science Biology Text Book
Pictures:
No comments:
Post a Comment